You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Democratic Operatives
- Thread starter GURPS
- Start date
LtownTaxpayer
Well-Known Member
You can't make this stuff up.
LightRoasted
If I may ...
For your consideration ...
Well, according to Maryland law, one must be at least 18 years of age before they can enter into a contract. In others words, they haven't reached the age of consent until they are 18 years of age.
Well, according to Maryland law, one must be at least 18 years of age before they can enter into a contract. In others words, they haven't reached the age of consent until they are 18 years of age.
WSJ: Dems In Disarray! No, Really!
If this is the status of their internal deliberations -- whether a Senate Democrat should have voted for Marco Rubio and Doug Burgum -- then they're worse off than we imagined. All they recognize at the moment is their impotence and have not yet even begun to recognize its source.
In one sense, that's understandable -- to a point. Democrats face a political environment unlike any they have seen in decades at least, and their credibility with voters has absolutely cratered in the wake of the Joe Biden Senility Cover-Up Scandal. The most recent Quinnipiac poll puts their favorability at 31/57, an all-time low, while Republicans score a more respectable 43/45. Why?
- "A majority of voters (60 percent) approve of sending U.S. troops to the southern border with Mexico to enforce border security, while 36 percent disapprove."
- On deportations, 44% support deporting all illegal aliens, and another 39% support deporting those convicted of crimes. Only six percent — six percent — oppose deportations.
- Sixty percent support sending the military to the southern border to secure it. Among independents, it’s 57/40, and even 29% of Democrats support that move.
Issue sets like immigration and foreign policy are one reason for the disarray. Democrats allowed themselves to get on the fringe on all of them, content in the knowledge that the progressive-elite clique that runs the media, Academia, and the bureaucracy had their back. What Democrats still have failed to recognize is that voters have lost trust not just in Democrats but in all of these institutions, to the point of existential crisis for all of them, not just the Democrats.
And that is because people finally got fed up with all of these institutions lying to and betraying them. That became most acute during the Joe Biden Regency, when anyone with eyes and ears understood that Biden was not in charge of anything, including his stage directions. He spent 40% of his presidency snoring on Rehoboth Beach while the bureaucracies and the Protection Racket Media insisted that Biden was "Sharp As A Tack!®" and "His Best Version" and not at all under orders from the Easter Bunny to get off the rope line. The media regurgitated the bureaucratic cabal's lies about "cheap fakes" making Biden look bad, rather than Biden clearly being incompetent in a way that anyone with an aging relative immediately grasped.
BREAKING: Federal Judge Orders Trump Admin to Restore Gender Ideology Websites
A group dubbed Doctors For America sued the Office of Personal Management and numerous government agencies, claiming the removal could prevent doctors from helping patients.
Judge Bates agreed with Doctors for America and ordered the extremist ideology to be restored.
“Defendants shall, in consultation with Plaintiff, identify any other resources that DFA members rely on to provide medical care and that defendants removed or substantially modified on or after January 29, 2025, without adequate notice or reasoned explanation; and defendants shall, by February 14, 2025, restore those resources to their versions as of January 30, 2025,” Judge John Bates wrote in an order reviewed by The Gateway Pundit.
Ousted From Power By Voters, Dems Turn To Activist Judges To Defy Trump
What all this lawfare amounts to is a kind of judicial coup against the sitting president. By doling out injunctions like they’re USAID grants for LGBTQ awareness programs in Mali, Democrats have been able to hamstring key aspects of Trump’s agenda — at least for the moment. It’s a simple enough tactic. All Democrats have to do is shop for a venue to find the most activist, rabidly anti-Trump federal judges in the country, file their lawsuits, and wait for the injunctions to come raining down.
By doing this, Democrats and their allies in the judiciary turn the Constitution on its head, and effectively govern negatively through injunction, making major reform of the federal bureaucracy impossible. In nearly every case so far, the federal judiciary is siding with the permanent bureaucracy in Washington, preventing the Trump administration from doing anything to reform it despite Trump having campaigned on precisely that promise.
The problem is, as my colleague Sean Davis noted recently on X, federal judges have no actual authority to do this. They can’t decide on their own who the president can talk to or what data he can access. They can’t bind the president at all. According to the U.S. Constitution they’re “inferior” courts and therefore don’t have any authority over the executive branch. Yes, the three branches of the federal government are coequal, but the only part of the federal judiciary that’s equal to the presidency is the Supreme Court, not all the federal district courts scattered across the country.
“John Roberts and SCOTUS have two options here: they can bring these inferior malcontents to heel, or they can get used to the President simply ignoring these inferior courts or Congress eliminating them entirely,” wrote Davis. “Congress created these inferior courts so the Supreme Court wouldn’t have to deal with every federal case by itself. But if these rogue inferior judges are going to routinely issue lawless decisions that the Supreme Court has to deal with anyway, Congress would be well within its rights to just eliminate them.”
The issue might come to a head before Congress gets around to eliminating the federal courts, though. If the Supreme Court steps in on just one of these cases where a federal judge has blocked a lawful executive order from Trump, it might not go well for Democrats. In the 2018 Supreme Court case Trump v. Hawaii, which reversed a lower court’s decision to uphold a nationwide injunction on Trump’s travel ban, Justice Clarence Thomas called into question the idea that a federal judge in Hawaii (or anywhere else) can simply issue an injunction against a presidential executive order and apply it to the entire country.
But now there’s someone in office who’s serious about changing it and who isn’t waving a white flag at the first bit of pushback from the judiciary. Under the radical theory that the executive branch of the federal government is in fact controlled by the executive (that’s the duly elected president), the Trump administration is appealing these court orders issued by unelected judges. And to the extent that the administration is defying them, there’s a non-obscure legal argument that they’re not even constitutional.
White House Deputy Chief of Staff Stephen Miller made that point in a social media post on Sunday. “Hey Pete,” he wrote in a response to former Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg, “care to show us the line in the Constitution where it says a lone unelected district judge can assume decision-making control over the entire executive branch affecting 300M citizens? Any mention of nationwide district court [temporary restraining orders]? Or permanent all-powerful bureaucracy?”
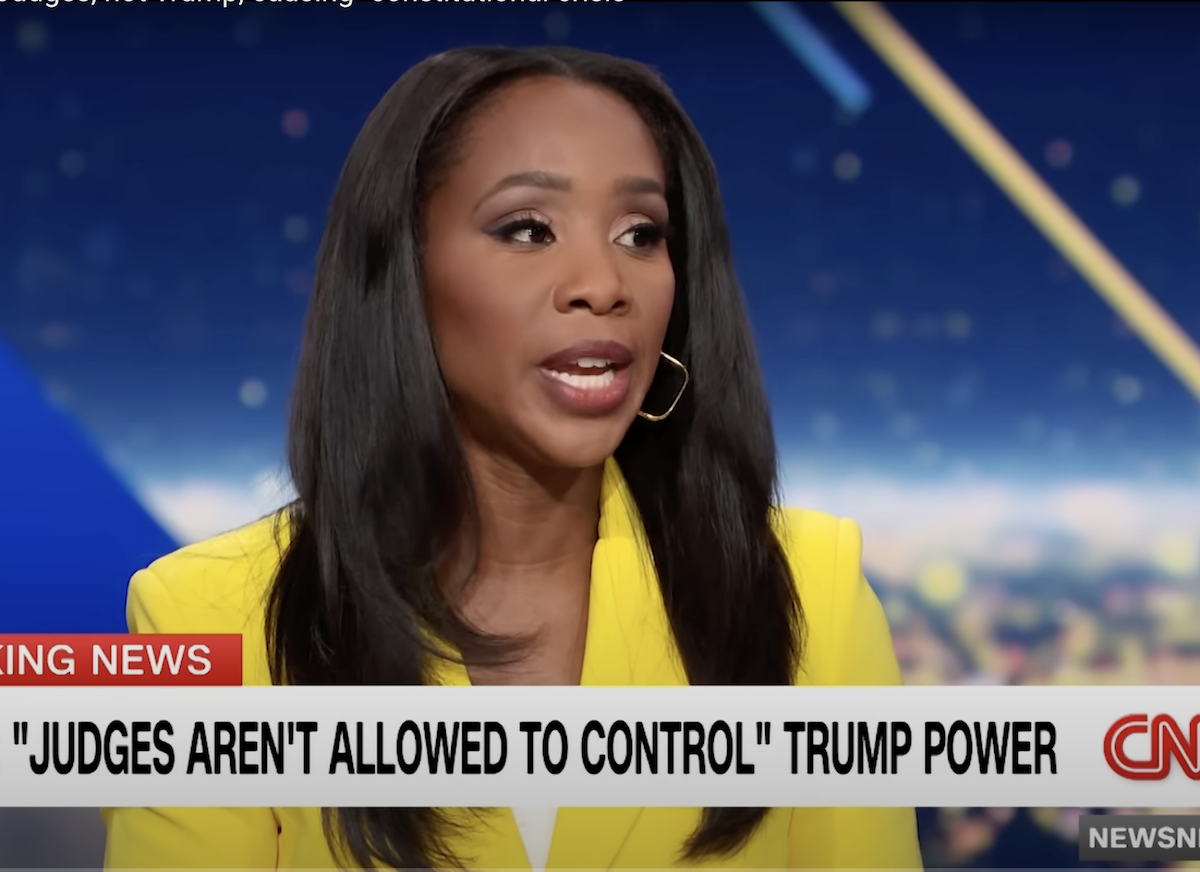
Vice President J.D. Vance similarly wrote on X, “Judges aren’t allowed to control the executive’s legitimate power.”
The short version of what’s been happening is Trump has issued a slew of executive orders directing federal agencies to do various things, some more controversial than others, like deny formal citizenship documents to the children of illegal aliens on U.S. soil. Democrat and activist judges have reacted by issuing their own orders compelling the administration to stop some of these policies, including — get this — a freeze on spending some money. Yes, a judge has demanded that the government spend money it literally doesn’t have. That’s where we are in this “constitutional crisis,” and we should think long and hard about who got us here.
Whether district judges even have the authority to issue a nationwide injunction orders is also up for debate. Justice Clarence Thomas in 2018 indicated the Supreme Court “must address their legality.” That’s what the Trump administration is hoping for.
None of this is a “crisis.” It’s the usual reaction from permanent Washington feeling its money and power under siege.
 thefederalist.com
thefederalist.com
White House Deputy Chief of Staff Stephen Miller made that point in a social media post on Sunday. “Hey Pete,” he wrote in a response to former Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg, “care to show us the line in the Constitution where it says a lone unelected district judge can assume decision-making control over the entire executive branch affecting 300M citizens? Any mention of nationwide district court [temporary restraining orders]? Or permanent all-powerful bureaucracy?”
Vice President J.D. Vance similarly wrote on X, “Judges aren’t allowed to control the executive’s legitimate power.”
The short version of what’s been happening is Trump has issued a slew of executive orders directing federal agencies to do various things, some more controversial than others, like deny formal citizenship documents to the children of illegal aliens on U.S. soil. Democrat and activist judges have reacted by issuing their own orders compelling the administration to stop some of these policies, including — get this — a freeze on spending some money. Yes, a judge has demanded that the government spend money it literally doesn’t have. That’s where we are in this “constitutional crisis,” and we should think long and hard about who got us here.
Whether district judges even have the authority to issue a nationwide injunction orders is also up for debate. Justice Clarence Thomas in 2018 indicated the Supreme Court “must address their legality.” That’s what the Trump administration is hoping for.
None of this is a “crisis.” It’s the usual reaction from permanent Washington feeling its money and power under siege.

How Media Learned To Start Worrying And Fear 'Constitutional Crisis'
None of this is a 'crisis.' It's the usual reaction from permanent Washington feeling its money and power under siege.
We've never heard of Congresswoman Maxine Dexter, be she seems to be part of The Resistance 2.0. She told a small crowd that she only had 30 seconds to speak, and decided to use that time to say, "We have to f**k Trump" and then blabber that her kids didn't see it. They won't see it on cable news, obviously, but if they're old enough to use X, chances are they'll stumble upon it, as it's making her famous.
She dropped the F-bomb on C-SPAN! That the best thing we've heard today since CNN's Dana Bash earnestly reporting on "Harry Bōlz."
We thought Rep. Waters was Mad Max, but here's Mad Maxine Dexter:


She dropped the F-bomb on C-SPAN! That the best thing we've heard today since CNN's Dana Bash earnestly reporting on "Harry Bōlz."
We thought Rep. Waters was Mad Max, but here's Mad Maxine Dexter:



